Table of Contents
As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, transitioning to renewable energy solutions has become a critical step towards achieving net zero emissions and mitigating its most devastating impacts.
The urgency to adopt carbon neutrality practices has never been more pressing, with the global community coming together to combat the climate crisis. By embracing renewable energy sources, we can significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
This shift towards a more sustainable future is not only an environmental imperative but also an economic opportunity, driving innovation and creating new industries.
Key Takeaways
- The transition to renewable energy is crucial for achieving net zero emissions.
- Carbon neutrality is key to mitigating climate change.
- Renewable energy solutions offer a pathway to a sustainable future.
- Adopting renewable energy sources reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- The shift to renewable energy drives innovation and creates new industries.
The Imperative of Net Zero: Understanding Carbon Neutrality
Achieving net zero emissions is now widely recognized as a critical step in mitigating the impacts of climate change. This goal has become a central focus for governments, businesses, and individuals worldwide.
Defining Net Zero Emissions in Today’s Context
Net zero emissions refer to a state where the amount of greenhouse gas emissions released into the atmosphere is balanced by the amount removed. This can be achieved through reducing emissions and implementing carbon sinks, such as reforestation efforts.
Climate Change Urgency and Scientific Consensus
The scientific community overwhelmingly agrees that human activities, particularly the emission of CO2 and other greenhouse gases, are significantly contributing to global warming. The urgency to act is underscored by the increasing frequency and severity of climate-related events.
Global and U.S. Net Zero Commitments Timeline
Many countries, including the United States, have committed to achieving net zero emissions by mid-century. The U.S. has set ambitious targets, with various states and cities also implementing their own strategies to reduce emissions and transition to renewable energy sources.
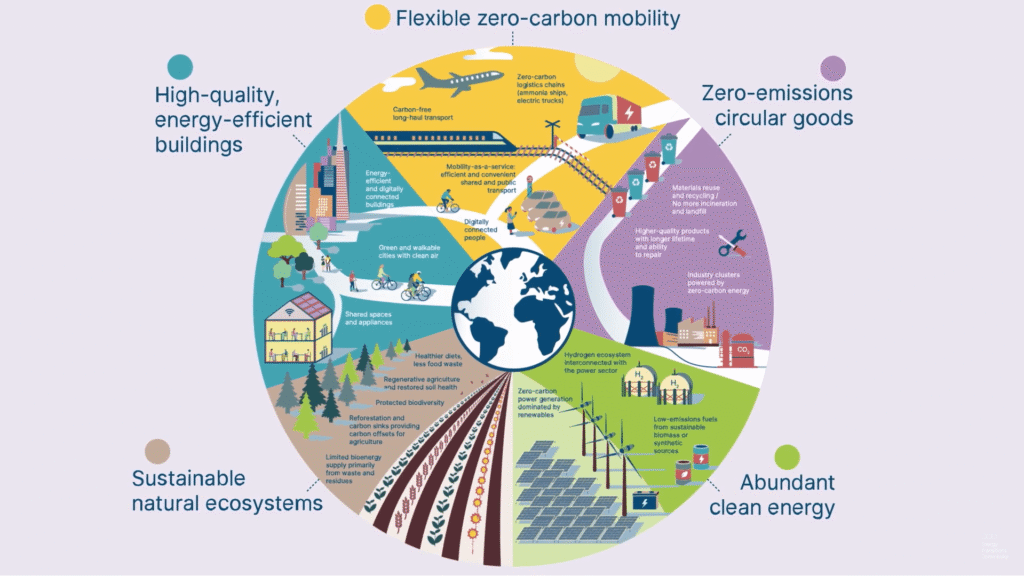
The transition to a net zero economy requires coordinated efforts across all sectors, including energy, transportation, and industry. By understanding the imperative of net zero emissions, we can better navigate the path towards a more sustainable future.
The Current State of Renewable Energy in the United States
Renewable energy is gaining momentum in the U.S., with substantial investments and innovative technologies transforming the energy landscape. This shift is driven by a combination of factors, including declining technology costs, increasing demand for clean energy, and supportive policies.
Renewable Energy Market Growth and Investment Trends
The U.S. renewable energy market has seen significant growth over the past decade, with renewable energy capacity increasing by over 50% since 2010. Investment trends indicate a continued shift towards solar and wind energy, with total investments reaching $55 billion in 2022. This growth is supported by federal and state-level policies, including tax credits and renewable portfolio standards.
Regional Adoption Patterns Across American States
Regional adoption of renewable energy varies significantly across the U.S., with states like California and Texas leading the way in solar and wind energy, respectively. The table below highlights the top five states for renewable energy capacity.
| State | Renewable Energy Capacity (GW) |
|---|---|
| California | 33.4 |
| Texas | 32.6 |
| Florida | 10.3 |
| North Carolina | 8.4 |
| Oregon | 7.4 |
U.S. Position in the Global Renewable Energy Landscape
The U.S. is a global leader in renewable energy, with significant investments in solar and wind technologies. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the U.S. ranks second globally in renewable energy capacity, behind China. The country’s commitment to renewable energy is expected to continue, driven by federal policies and state-level initiatives.
Solar Power: Harnessing the Sun’s Potential
Harnessing the sun’s energy has become a crucial strategy in the transition to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy mix. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, solar power is emerging as a vital component of the global energy landscape.
Latest Photovoltaic Technology Advancements
The photovoltaic (PV) industry has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, leading to more efficient and cost-effective solar panels. Bifacial solar panels, for example, can capture sunlight from both the front and back sides of the panel, increasing energy output by up to 25%. Additionally, advancements in perovskite solar cells are promising to further boost efficiency and reduce production costs.
Utility-Scale Solar Projects Transforming the Grid
Utility-scale solar projects are playing a crucial role in transforming the energy grid. These large-scale installations are capable of generating significant amounts of electricity, contributing to grid stability and helping to meet peak demand. One of the notable examples is the Solar Star project in California, which is one of the largest solar farms in the world.
| Project Name | Location | Capacity (MW) |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Star | California, USA | 579 |
| Pavagada Solar Park | Karnataka, India | 2050 |
| Desert Sunlight Solar Farm | California, USA | 550 |
Residential and Commercial Solar Applications
Solar energy is not just limited to utility-scale projects; it is also being increasingly adopted in residential and commercial settings. Homeowners and businesses are turning to solar power to reduce their energy bills and carbon footprint. Incentives and financing models have made it more accessible for individuals and companies to invest in solar energy.
Solar Financing Models and Incentives
Various financing models and incentives are available to support the adoption of solar energy. These include tax credits, grants, and power purchase agreements (PPAs). Such incentives help reduce the upfront costs of solar installations, making it more viable for a wider audience.
Wind Energy: Capturing the Power of Air in Motion
The potential of wind energy to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable development is vast. As the world shifts towards cleaner energy sources, wind power is emerging as a vital component in the renewable energy mix.
Onshore Wind Farm Developments and Expansion
Onshore wind farms continue to be a significant source of renewable energy. Recent advancements in turbine technology have improved efficiency and reduced costs, making onshore wind a competitive option in the energy market. Large-scale wind farms are being developed across various regions in the United States, contributing to the country’s renewable energy targets.
Offshore Wind Opportunities Along U.S. Coastlines
Offshore wind energy presents a substantial opportunity for growth. The U.S. coastline offers vast areas suitable for offshore wind farms, which can generate significant amounts of electricity. Offshore wind projects are being planned and developed along the East Coast, with several pilot projects already underway.
Small-Scale Wind Solutions for Distributed Generation
Small-scale wind solutions are becoming increasingly popular for distributed generation. These systems can be used for residential, commercial, or agricultural purposes, providing a decentralized source of renewable energy. Advancements in small turbine technology have made these systems more efficient and affordable.
Wind Technology Efficiency Improvements
Improvements in wind technology have been instrumental in enhancing the efficiency of wind energy production. Larger turbines with advanced blade designs and smart wind farm management systems are some of the innovations driving this progress. These advancements are crucial for maximizing the potential of wind energy.
Hydroelectric and Marine Energy: Utilizing Water Resources
Harnessing the power of water through hydroelectric and marine energy is a vital step towards a sustainable future. As the world continues to transition towards cleaner energy sources, the importance of these renewable energy forms cannot be overstated.
Modern Hydropower Systems and Upgrades
Modern hydropower systems have evolved significantly, incorporating advanced technologies to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Upgrades to existing infrastructure have enabled the optimization of energy production while minimizing ecological disruption. For instance, the implementation of fish-friendly turbines has significantly reduced the mortality rate of fish passing through dams.
Emerging Tidal and Wave Energy Technologies
Tidal and wave energy technologies are emerging as promising sources of renewable energy. These technologies harness the predictable and cyclical nature of ocean tides and waves to generate electricity. Ocean Energy Systems are being developed to capture this energy, providing a consistent and reliable source of power.
Environmental Considerations and Fish-Friendly Designs
The development of hydroelectric and marine energy facilities requires careful consideration of environmental impacts. Designs that incorporate fish-friendly features and minimize habitat disruption are crucial. For example, some modern dams now include fish ladders to facilitate the migration of fish species.
By embracing these technologies and design considerations, we can ensure that hydroelectric and marine energy contribute significantly to our renewable energy portfolio while protecting the environment.
Geothermal and Biomass: Alternative Renewable Sources
As the world shifts towards renewable energy, geothermal and biomass emerge as vital alternative sources. These energy forms are crucial in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
Geothermal Heat Extraction Methods and Applications
Geothermal energy harnesses heat from the Earth’s interior. Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) and traditional hydrothermal systems are key technologies used for geothermal heat extraction. EGS, in particular, offers the potential to expand geothermal development beyond conventional hydrothermal resources.
Sustainable Biomass Conversion Technologies
Biomass energy is derived from organic materials such as wood, crops, and waste. Sustainable biomass conversion involves technologies like anaerobic digestion, gasification, and combustion to produce electricity, heat, or biofuels. These technologies offer a low-carbon alternative for energy production.
Carbon Neutrality Assessment of Various Feedstocks
Assessing the carbon neutrality of biomass feedstocks is essential. Factors such as land use change, production processes, and energy conversion efficiency are considered. Carbon-neutral biomass can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions when used in place of fossil fuels.
The integration of geothermal and biomass energy into our energy mix can significantly contribute to achieving carbon neutrality. By leveraging these alternative renewable sources, we can create a more sustainable energy future.
- Geothermal energy offers a reliable and constant power supply.
- Biomass energy provides a versatile range of energy products.
- Both energy sources contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Renewable Energy Solutions for Achieving Net Zero Goals
The path to achieving net zero goals is paved with innovative renewable energy solutions that transform the way we generate and consume energy. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, the importance of transitioning to a sustainable energy future has never been more pressing.
Integrated Energy Systems Design and Implementation
Integrated energy systems are crucial for optimizing energy distribution and consumption. By combining different renewable energy sources and storage technologies, these systems can provide a stable and reliable energy supply. Effective implementation requires careful planning, advanced technologies, and a deep understanding of local energy needs.
Advanced Energy Storage Technologies
Advanced energy storage technologies play a vital role in supporting the widespread adoption of renewable energy. Innovations in battery technology, such as lithium-ion batteries, and other storage solutions like pumped hydro storage, are critical for addressing the intermittency of renewable energy sources.
Smart Grid Infrastructure and Digital Management
The integration of smart grid infrastructure and digital management systems is essential for managing the complexities of renewable energy distribution. Smart grids enable real-time monitoring and control, enhancing grid resilience and efficiency.
Microgrids and Resilient Decentralized Energy Networks
Microgrids and decentralized energy networks offer a resilient and flexible approach to energy management. By enabling local energy generation and consumption, these systems can reduce reliance on centralized power grids and enhance energy security.
In conclusion, achieving net zero goals requires a comprehensive approach to renewable energy solutions, including integrated energy systems, advanced energy storage, smart grid infrastructure, and microgrids. By leveraging these technologies, we can create a more sustainable, resilient, and decentralized energy future.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation from Renewable Energy
As the world shifts towards renewable energy, the economic benefits are becoming increasingly evident, from job creation to infrastructure development. The renewable energy sector is proving to be a significant contributor to economic growth, offering a promising alternative to traditional energy sources.
Employment Statistics
The renewable energy industry has seen substantial job growth in recent years. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the sector supported over 11 million jobs worldwide in 2022, with solar and wind energy being the largest employers. In the United States, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that employment in renewable energy is projected to grow by 10% through 2030, outpacing many other industries.
“The renewable energy sector is not just about reducing carbon emissions; it’s also about creating economic opportunities and jobs that can’t be outsourced.” –
Economic Multiplier Effects
Renewable energy projects have a multiplier effect on local economies. A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) found that every dollar invested in renewable energy generates between $1.40 and $3.50 in local economic activity. This is due to the creation of new industries, jobs, and infrastructure, which in turn stimulate local spending and economic growth.
Cost Comparisons
The cost of renewable energy has decreased dramatically over the past decade, making it more competitive with conventional energy sources. The cost of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, for example, has fallen by over 70% since 2010. According to a report by Lazard, the levelized cost of electricity from solar PV is now often lower than that of coal and gas-fired power plants.
Long-term Sustainability Projections
Projections indicate that the transition to renewable energy will continue to drive economic growth and job creation in the long term. As technology improves and economies of scale are achieved through larger production volumes, the cost of renewable energy is expected to continue its downward trend, making it an increasingly viable option for both developed and developing economies.
In conclusion, the economic benefits of renewable energy are multifaceted, ranging from job creation and economic multiplier effects to cost competitiveness and long-term sustainability. As the world continues to transition towards a more renewable energy-based economy, these benefits are likely to grow, supporting a more sustainable and equitable future.
Implementation Strategies for Businesses and Communities
The transition to renewable energy requires innovative implementation strategies that cater to the diverse needs of businesses and communities. As the world moves towards achieving net zero emissions, the importance of effective and tailored approaches to renewable energy adoption cannot be overstated.
Corporate Renewable Energy Procurement Models
Corporate renewable energy procurement models have gained significant traction as companies seek to reduce their carbon footprint. These models include power purchase agreements (PPAs), renewable energy certificates (RECs), and on-site renewable installations. For instance, tech giants like Google and Microsoft have signed large-scale PPAs to power their data centers with renewable energy.
Community-Owned Renewable Energy Projects
Community-owned renewable energy projects empower local communities to take charge of their energy future. These projects not only provide clean energy but also generate revenue and create jobs within the community. Examples include community solar gardens and cooperative wind farms.
Public-Private Partnerships for Large-Scale Deployment
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) play a crucial role in accelerating the deployment of renewable energy technologies. By combining the strengths of both sectors, PPPs can mobilize significant investment, drive innovation, and overcome regulatory barriers. A notable example is the partnership between the U.S. Department of Energy and various private companies to develop advanced solar technologies.
Case Studies: Successful Business Transitions to Renewables
Several businesses have successfully transitioned to renewable energy, serving as models for others. For example, Walmart has committed to powering 50% of its stores with renewable energy by 2025, while IKEA aims to be 100% renewable by 2030. These case studies demonstrate the feasibility and benefits of transitioning to renewable energy.
“Renewable energy is becoming increasingly cost-competitive with fossil fuels, making it an attractive option for businesses looking to reduce their energy costs and carbon footprint.”
By adopting these implementation strategies, businesses and communities can accelerate their transition to renewable energy, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Policy Frameworks and Financial Incentives
Effective policy frameworks and financial incentives are crucial for accelerating the adoption of renewable energy technologies. A comprehensive policy framework can provide the necessary stability and predictability for investors and developers.
Federal Renewable Energy Policies and the Inflation Reduction Act
The Inflation Reduction Act represents a significant step forward in U.S. federal policy regarding renewable energy. It includes provisions for tax credits, grants, and other financial incentives aimed at reducing the cost of renewable energy technologies and encouraging investment in the sector.
- Extended tax credits for solar and wind energy projects
- Grants for clean energy manufacturing and deployment
- Funding for climate resilience and adaptation efforts
State-Level Renewable Portfolio Standards
State-level Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) have been instrumental in driving renewable energy adoption across the United States. These standards require utilities to generate a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources.
Key aspects of RPS include:
- Varied targets across states, reflecting local renewable energy potential
- Mechanisms for compliance, such as renewable energy certificates (RECs)
- Penalties for non-compliance to ensure enforcement
Tax Credits, Grants, and Financing Mechanisms
Financial incentives are critical for reducing the upfront costs associated with renewable energy projects. Tax credits, grants, and specialized financing mechanisms can make these projects more viable.
International Policy Comparisons and Best Practices
Comparing international policies can provide valuable insights into effective strategies for promoting renewable energy. Countries with strong renewable energy policies often share certain best practices.
“Countries that have successfully integrated high levels of renewable energy into their grids often have robust policy frameworks in place, including stable long-term targets and incentives for investment.”
By examining these policies and adapting them to the U.S. context, policymakers can develop more effective strategies for achieving net-zero goals.
Conclusion: Charting the Path to a Renewable Future
As the world moves towards achieving net zero emissions, the importance of renewable energy solutions cannot be overstated. The transition to a renewable future is crucial for promoting sustainable energy and mitigating climate change. By harnessing the potential of solar, wind, hydro, and other renewable sources, the United States can significantly reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
The economic benefits of renewable energy are also substantial, with the sector creating new job opportunities and stimulating local economies. To accelerate the transition to a renewable future, it is essential to implement effective policy frameworks, invest in advanced energy storage technologies, and develop smart grid infrastructure.
By working together to chart a path towards a renewable future, we can create a more sustainable energy landscape and achieve net zero emissions. This requires a continued commitment to innovation, investment, and collaboration across industries and communities.