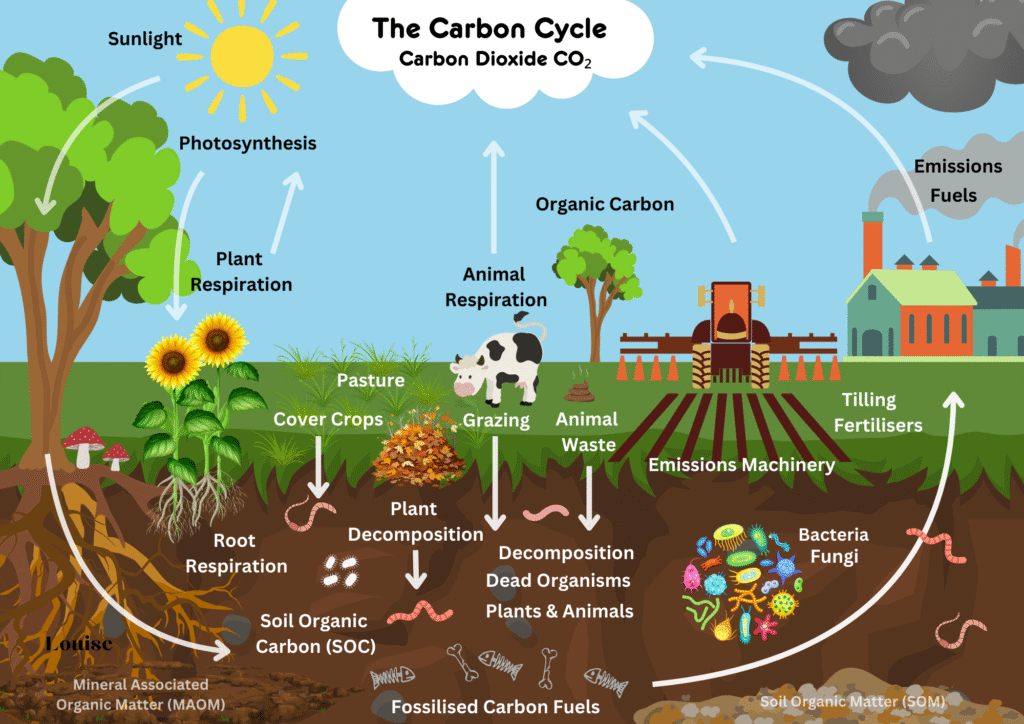
Achieving Net Zero Carbon is becoming increasingly crucial in the agricultural sector. Farmers and agricultural practices play a significant role in greenhouse gas emissions, making it essential to adopt sustainable agriculture methods.
The agricultural industry is under pressure to reduce its carbon footprint. Implementing emission reduction techniques is vital for a sustainable future. This involves adopting innovative farming practices and technologies that minimize environmental impact.
By transitioning to more sustainable practices, farmers can significantly contribute to reducing global emissions. This not only benefits the environment but also enhances the long-term viability of agricultural businesses.
key Takeaways
- Adopting sustainable agriculture practices is crucial for reducing emissions.
- Farmers play a vital role in achieving Net Zero Carbon.
- Implementing emission reduction techniques is essential for a sustainable agricultural industry.
- Sustainable practices can enhance the long-term viability of agricultural businesses.
- Innovative farming practices and technologies can minimize environmental impact.
The Climate Challenge in Agriculture
The US agricultural industry is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, and reducing these emissions is crucial for mitigating climate change. Agriculture accounts for approximately 10% of the total US greenhouse gas emissions, with the majority coming from livestock and crop production.
Current Emission Levels in US Agriculture
The agricultural sector in the US is responsible for emitting substantial amounts of greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. These emissions are primarily due to practices such as livestock production, fertilizer use, and tillage.
Why Net Zero Carbon Matters for Farmers
Achieving net zero carbon is crucial for farmers as it not only contributes to mitigating climate change but also enhances their resilience to its impacts. By reducing their carbon footprint, farmers can improve soil health, reduce water usage, and increase biodiversity on their farms.
The Economic Case for Emission Reduction
Reducing emissions can also have economic benefits for farmers. By adopting more efficient practices and reducing waste, farmers can lower their operational costs and potentially access new markets and incentives for sustainable production. Moreover, as consumers increasingly demand more climate-friendly products, farmers who reduce their emissions can gain a competitive edge.
In conclusion, addressing the climate challenge in agriculture requires a multifaceted approach that includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adopting more sustainable agricultural practices. By understanding the current emission levels, the importance of achieving net zero carbon, and the economic benefits of emission reduction, farmers and policymakers can work together to create a more sustainable agricultural sector.
Understanding Agricultural Carbon Footprint
Understanding the sources and extent of agricultural carbon footprint is vital for developing effective emission reduction strategies. The agricultural sector is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, and recognizing the areas that need improvement is the first step towards sustainability.
Major Sources of Emissions in Farming
Farming activities emit substantial amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). Major sources include the use of fertilizers and pesticides, livestock digestion, and the operation of farm machinery. These activities contribute to the overall carbon footprint of agricultural practices.
Measuring Your Farm’s Carbon Impact
To effectively reduce emissions, farmers must first measure their farm’s carbon footprint. This involves assessing energy consumption, soil health, and livestock management practices. Tools and calculators are available to help farmers quantify their emissions and identify areas for improvement.
Setting Realistic Reduction Targets
Once the carbon footprint is measured, setting realistic reduction targets is crucial. This involves adopting emission reduction techniques such as regenerative agriculture, improving energy efficiency, and implementing sustainable livestock management practices. By setting achievable goals, farmers can make steady progress towards reducing their environmental impact.
By understanding and addressing the carbon footprint of agricultural practices, farmers can contribute to a more sustainable food system while also improving their bottom line through more efficient practices.
Soil Management Practices for Carbon Sequestration
Agricultural soils have the potential to act as significant carbon sinks through proper management. By adopting sustainable practices, farmers can enhance soil carbon sequestration, contributing to a reduction in atmospheric CO2 levels.
No-Till and Reduced Tillage Methods
No-till and reduced tillage methods minimize soil disturbance, preserving soil organic matter and reducing erosion. This approach not only enhances carbon sequestration but also improves soil health and water retention. Studies have shown that no-till farming can increase soil carbon by up to 30% over conventional tillage methods.
Cover Cropping Strategies
Cover cropping involves planting crops between crop cycles to protect and enrich the soil. These crops help in capturing atmospheric carbon dioxide and converting it into soil organic matter. Leguminous cover crops, for instance, add nitrogen to the soil, further enhancing its fertility.
Biochar and Soil Amendments
Biochar, a form of charcoal, is produced by heating organic material in a low-oxygen environment. When added to soil, it can significantly improve soil fertility and carbon sequestration. The long-term carbon storage potential of biochar makes it a valuable tool in the fight against climate change.
Application Techniques for Maximum Benefit
The effectiveness of biochar and other soil amendments depends on their application techniques. Proper mixing and incorporation into the soil are crucial for maximizing their benefits. Farmers should consider factors like soil type and crop selection when applying these amendments.
By combining these soil management practices, farmers can not only enhance carbon sequestration but also improve the overall health and productivity of their soils.
Livestock Management to Reduce Methane Emissions
Methane emissions from livestock can be significantly reduced through strategic management practices. Livestock, particularly ruminant animals like cows and sheep, are significant contributors to methane emissions due to their digestive processes. However, by optimizing livestock management, farmers can reduce these emissions while maintaining productivity.
Feed Optimization Techniques
One effective method for reducing methane emissions is through feed optimization. By improving the quality and digestibility of feed, farmers can decrease the amount of methane produced during digestion. For instance, adding certain fats or oils to feed can help reduce methane emissions. As Dr. Jane Smith, an animal nutritionist, notes, “Feed optimization not only reduces emissions but can also improve animal health and productivity.”
- Incorporating high-quality forages into diets
- Using feed additives that mitigate methane production
- Optimizing feed delivery systems to reduce waste
Manure Management Systems
Effective manure management is another critical aspect of reducing methane emissions from livestock. Manure decomposition can produce significant amounts of methane, especially under anaerobic conditions. Implementing systems that capture and utilize methane from manure, such as anaerobic digesters, can significantly reduce emissions.
Anaerobic digesters are particularly effective as they not only reduce methane emissions but also produce biogas, which can be used as renewable energy. According to
“The use of anaerobic digesters on farms can reduce greenhouse gas emissions while generating clean energy.” – USDA
Grazing Rotation Practices
Grazing rotation practices can also play a crucial role in mitigating methane emissions. By rotating grazing areas, farmers can improve pasture health and reduce the amount of methane produced per unit of production. This practice also helps in sequestering carbon in soils.
Monitoring and Measuring Emission Reductions
To ensure the effectiveness of these strategies, it’s essential to monitor and measure emission reductions. Techniques such as using GreenFeed systems or other methane measurement tools can provide valuable data on the impact of different management practices on methane emissions. Regular monitoring allows farmers to adjust their strategies and achieve better outcomes.
| Management Practice | Methane Reduction Potential |
|---|---|
| Feed Optimization | 10-20% |
| Manure Management | 50-70% |
| Grazing Rotation | 5-15% |
Net Zero Carbon in Agriculture: Techniques to Reduce Emissions
Net zero carbon in agriculture is within reach through the adoption of precision agriculture, renewable energy, and carbon offsetting. As the agricultural sector continues to evolve, it’s crucial to implement practices that not only reduce emissions but also promote sustainability.
Precision Agriculture Technologies
Precision agriculture involves the use of advanced technologies to optimize farming practices. This includes:
GPS and Sensor-Based Farming
GPS and sensor-based farming allows for precise application of resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides. This not only reduces waste but also minimizes the environmental impact of farming activities.
Variable Rate Applications
Variable rate applications enable farmers to apply inputs at different rates across a field, based on specific conditions. This technique helps in reducing the overuse of resources and lowering emissions.
Renewable Energy Integration
Integrating renewable energy sources into farming operations is another effective way to reduce carbon emissions. Solar panels and wind turbines can provide the energy needed for farm operations, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Solar energy for powering irrigation systems and farm equipment.
- Wind energy for generating electricity for farm use.
Carbon Offsetting Strategies
Carbon offsetting involves compensating for emissions by investing in projects that reduce greenhouse gases elsewhere. For agriculture, this could mean:
- Investing in reforestation or afforestation projects.
- Supporting renewable energy projects.
- Implementing soil carbon sequestration practices.
By adopting these techniques, farmers can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to achieving net zero emissions in agriculture.
Crop Selection and Management for Lower Emissions
Effective crop selection and management are crucial for reducing agricultural emissions. By choosing the right crops and implementing sustainable practices, farmers can significantly lower their carbon footprint.
Climate-Smart Crop Varieties
Using climate-smart crops is a strategy that can help farmers adapt to climate change while reducing emissions. These crops are bred to be more resilient to changing weather patterns and can thrive in challenging conditions. Examples include drought-tolerant varieties and crops with improved pest resistance.
Nitrogen-Efficient Farming Practices
Nitrogen-efficient farming practices are essential for reducing nitrous oxide emissions, a potent greenhouse gas. Techniques such as precision agriculture and the use of nitrogen-fixing crops can help minimize nitrogen waste. By optimizing nitrogen use, farmers can lower their emissions while maintaining crop yields.
Agroforestry Integration
Agroforestry involves integrating trees into farming systems, which can help sequester carbon dioxide. This practice also promotes biodiversity and can improve soil health.
Silvopasture Systems for US Farms
A specific form of agroforestry, silvopasture systems combine trees with livestock grazing. This approach can enhance carbon sequestration, improve animal welfare, and increase farm productivity.
| Practice | Emission Reduction Potential | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Climate-Smart Crops | Moderate | Improved resilience, increased yields |
| Nitrogen-Efficient Practices | High | Reduced nitrogen waste, cost savings |
| Agroforestry Integration | High | Biodiversity promotion, soil health improvement |
Water Management and Irrigation Efficiency
As agriculture moves towards net zero carbon, optimizing water use is becoming increasingly important. Effective water management not only conserves this vital resource but also reduces the energy required for irrigation, thereby lowering overall emissions.
Drip Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to the roots of plants, minimizing evaporation and runoff. This method can significantly reduce water usage compared to traditional sprinkler systems. According to the USDA, adopting drip irrigation can cut water consumption by up to 50%.
Water Recycling Techniques
Implementing water recycling techniques in agriculture can further enhance water efficiency. Techniques such as using treated wastewater for irrigation not only conserve freshwater resources but also reduce the environmental impact of agricultural runoff.
Reducing Energy for Pumping
Reducing the energy required for water pumping is another critical aspect of improving irrigation efficiency. Using renewable energy sources, such as solar-powered pumps, can significantly lower the carbon footprint associated with irrigation.
| Irrigation Method | Water Savings | Energy Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation | Up to 50% | 30-50% |
| Water Recycling | 20-30% | 10-20% |
| Solar-Powered Pumps | N/A | Up to 100% |
By adopting these strategies, farmers can significantly improve sustainable agriculture practices, contributing to the overall goal of net zero carbon emissions.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Achieving Net Zero Carbon in agriculture requires overcoming several implementation challenges, including financial, educational, and scalability issues. Farmers and agricultural stakeholders must navigate these obstacles to successfully reduce emissions.
Financial Barriers and Funding Options
One of the significant challenges is the financial burden associated with adopting new, emission-reducing technologies and practices. Initial investment costs can be prohibitive for many farmers. However, various funding options and incentives are available to help mitigate these costs.
- Government grants and subsidies for sustainable agriculture practices
- Low-interest loans for farmers adopting climate-friendly technologies
- Private investment in sustainable agriculture projects
Knowledge Gaps and Educational Resources
Another challenge is the lack of knowledge about the most effective emission reduction strategies. Educational resources and training programs can bridge this gap. Extension services and online platforms offering guidance on best practices are crucial.
“Education is the key to unlocking the potential for sustainable agriculture practices.”
Scaling Solutions for Different Farm Sizes
Solutions must be scalable to accommodate farms of different sizes. Precision agriculture technologies and flexible management practices can be adapted to various farm sizes, ensuring that all farmers can contribute to emission reductions.
| Farm Size | Scalable Solutions |
|---|---|
| Small Farms | Drip irrigation, cover cropping |
| Medium Farms | Precision agriculture, manure management |
| Large Farms | Renewable energy integration, agroforestry |
Economic Incentives and Carbon Markets
With the growing focus on climate change, farmers can leverage carbon markets and government support to enhance their sustainability and profitability. As the agricultural sector continues to evolve, understanding and utilizing these economic incentives becomes increasingly important for farmers looking to adopt low-carbon practices.
Carbon Credit Programs for US Farmers
Carbon credit programs offer a financial incentive for farmers to reduce their carbon footprint. By implementing practices such as no-till farming, cover cropping, and reforestation, farmers can sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, earning them carbon credits. These credits can then be sold on carbon markets to companies looking to offset their emissions.
For instance, programs like the USDA’s Climate Hubs provide resources and guidance for farmers to participate in carbon credit programs. Farmers can work with aggregators or directly with companies to sell their carbon credits, creating an additional revenue stream.
Federal and State Support Programs
Beyond carbon credits, federal and state governments offer various support programs to encourage sustainable farming practices. These can include grants, subsidies, and technical assistance to help farmers transition to more sustainable practices.
- The Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) provides financial assistance to farmers adopting conservation practices.
- The Conservation Stewardship Program (CSP) rewards farmers for maintaining and improving their existing conservation efforts.
These programs not only help farmers financially but also enhance their environmental stewardship.
Consumer-Driven Market Opportunities
Consumers are increasingly demanding products that are sustainably produced, creating market opportunities for farmers who adopt low-carbon practices. By marketing their products as environmentally friendly, farmers can tap into this growing market.
Marketing Your Low-Carbon Agricultural Products
To capitalize on consumer demand, farmers should consider the following strategies:
- Certification: Obtain certifications like USDA Organic or Regenerative Organic Certified to validate your sustainable practices.
- Labeling: Clearly label your products with environmental claims, ensuring they are substantiated by credible data.
- Storytelling: Share your sustainability story with consumers through various marketing channels to build brand loyalty.
By effectively marketing their low-carbon products, farmers can differentiate themselves in the market and potentially command a premium price.
Conclusion: The Path Forward to Net Zero Agriculture
Achieving net zero carbon in agriculture is crucial for mitigating climate change and ensuring a sustainable food system. The techniques outlined in this article, from soil management practices to livestock management and precision agriculture, offer a comprehensive approach to reducing emissions.
Farmers, policymakers, and consumers must work together to drive this change. By adopting sustainable agriculture practices, supporting climate-resilient farming, and promoting net zero agriculture initiatives, we can create a more environmentally friendly and economically viable agricultural sector.
The transition to net zero agriculture not only addresses climate change but also enhances the long-term sustainability of our food systems. As we move forward, it’s essential to continue developing and implementing effective strategies that support this goal, ultimately contributing to a healthier planet.